In short, concurrency refers to the number of API requests you can have in progress (or running) simultaneously. If your plan supports 5 concurrent requests, you can process up to 5 requests simultaneously. You’ll get an error if you send a sixth request while five are already processing.
Understanding Concurrency
Concurrency is a fundamental concept in web scraping, referring to the ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. In the context of ZenRows, it defines how many scraping requests can be processed at the same time. Think of concurrency like a team of workers in a factory. Each worker represents a “concurrent request slot.” If you have 5 workers, you can assign them 5 tasks (or requests) simultaneously. If you try to assign a 6th task while all workers are occupied, you will need to wait until one of them finishes their current task before the new one can be started. In ZenRows, each “task” is an API request, and each “worker” is a concurrent request slot available to you based on your subscription.Impact of Request Duration on Throughput
The duration that each request takes to complete significantly influences how many requests you can process in a given timeframe. This concept is crucial for optimizing your scraping efficiency and maximizing throughput. Here’s how it works:- Fast Requests: If each request takes 1 second to complete and you have 5 concurrent slots available, you can process 5 requests every second. Over a 60-second period, this means you can handle 300 requests (5 requests/second × 60 seconds).
- Slow Requests: Conversely, if each request takes 10 seconds to complete, you can process 5 requests every 10 seconds. Over the same 60-second period, you’ll only manage 30 requests (5 requests/10 seconds × 60 seconds).
Example Scenario
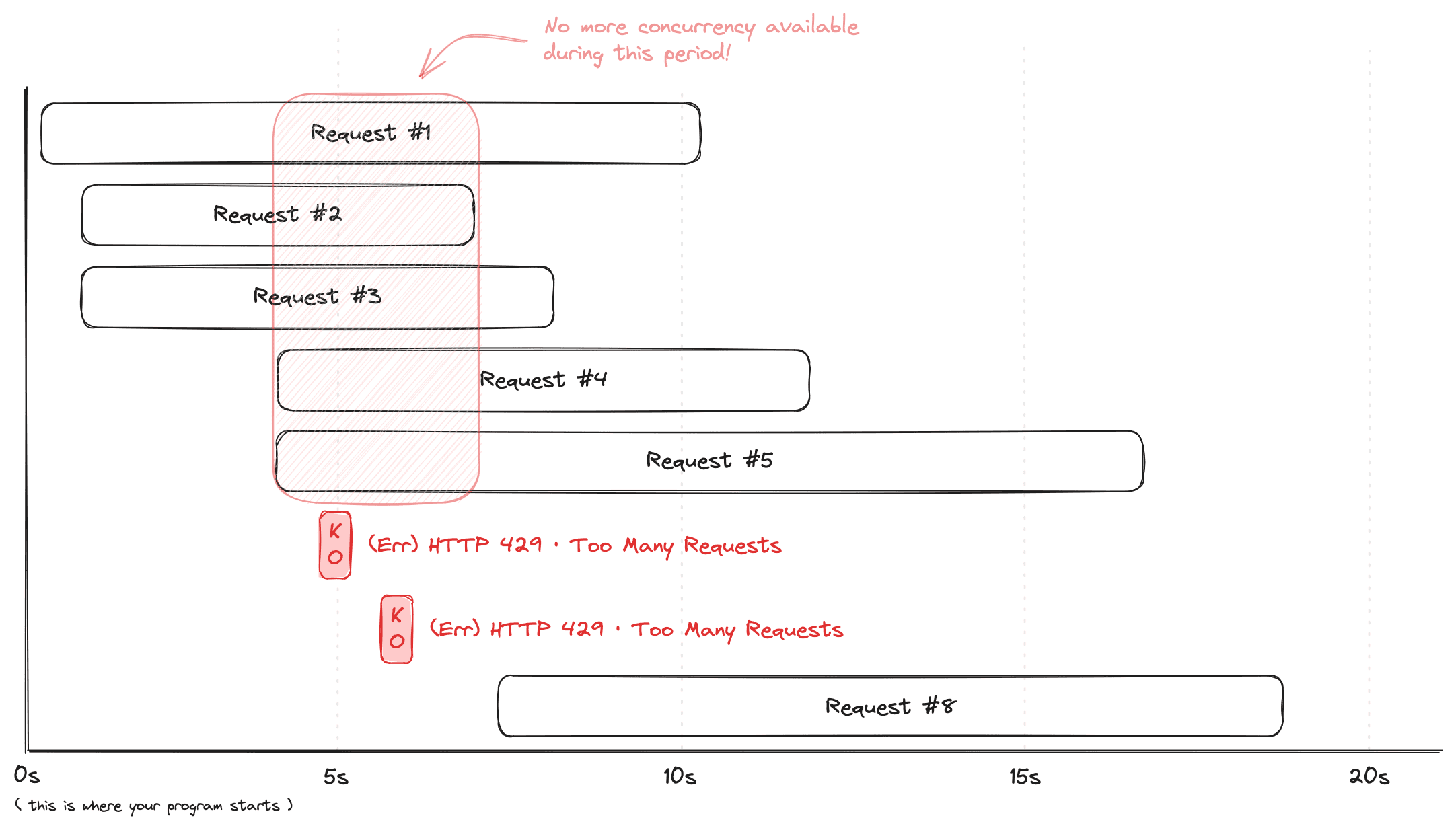
To better understand this, consider a situation where your plan allows 5 concurrent requests: Scenario:- 1st Request: Takes 10 seconds to finish.
- 2nd Request: Takes 7 seconds to finish.
- 3rd Request: Takes 8 seconds to finish.
- 4th Request: Takes 9 seconds to finish.
- 5th Request: Takes 14 seconds to finish.
- 6th & 7th Request: Since all 5 slots are occupied, you will receive “429 Too Many Requests” errors. The system can only process additional requests once one of the initial 5 requests finishes. In this example, the quickest request (the 2nd request) completes in 7 seconds, freeing up a slot for new requests.
Concurrency Headers
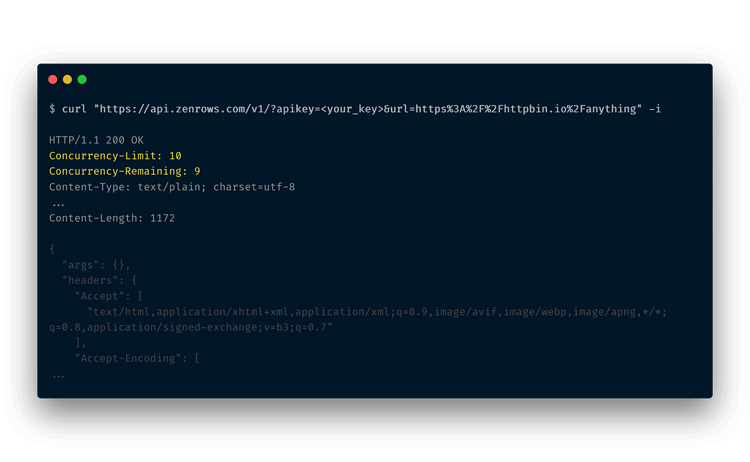
To help you manage and optimize your API usage, each response from our API includes two important HTTP headers related to concurrency:Concurrency-Limit: Indicates the total number of concurrent requests allowed by your current plan. This header helps you understand the maximum concurrency capacity available to you.Concurrency-Remaining: Shows the number of available concurrency slots at the time the request was received by the server. This provides insight into how many slots are still free.
Concurrency-Limit: 20Concurrency-Remaining: 17
Using Concurrency Headers for Optimization
These headers are valuable tools for optimizing your scraping tasks. By monitoring and interpreting these headers in real time, you can adjust your request patterns to make the most efficient use of your concurrency slots. Optimization Tips:- Before sending a batch of requests, inspect the
Concurrency-Remainingheader of the most recent response. - Based on the value of this header, adjust the number of parallel requests you send. For example, if
Concurrency-Remainingis 5, avoid sending more than 5 simultaneous requests.
Using Concurrency
ZenRows SDK for Python
To run the examples, ensure you have Python 3 installed. Install the necessary libraries with:asyncio.gather function will wait for all the calls to finish and store all the responses in an array. Afterward, you can loop over the array and extract the necessary data. Each response will include the status, request, response content, and other values. Remember to run the scripts with asyncio.run to avoid a coroutine 'main' was never awaited error.
scraper.py
Python with requests
If you prefer using the requests library and want to handle multiple requests concurrently, Python’s multiprocessing package can be an effective solution. This approach is particularly useful when you’re dealing with a large list of URLs and need to speed up the data collection process by sending multiple requests simultaneously.
multiprocessing package in Python includes a ThreadPool class, which allows you to manage a pool of worker threads. Each thread can handle a separate task, enabling multiple HTTP requests to be processed in parallel. This is particularly beneficial when scraping data from a large number of websites, as it reduces the overall time required.
scraper.py
ZenRows SDK for JavaScript
When working with JavaScript for web scraping, managing concurrency and handling retries can be challenging. The ZenRows JavaScript SDK simplifies these tasks by providing built-in concurrency and retry options. This is particularly useful for developers who need to scrape multiple URLs efficiently while avoiding rate limits. To get started, install the ZenRows SDK using npm:fulfilled and rejected responses separately, allowing you to log errors or retry failed requests as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does concurrency affect the speed of scraping tasks?
How does concurrency affect the speed of scraping tasks?
Concurrency directly influences how many tasks can be handled at the same time, meaning higher concurrency results in faster scraping as multiple requests can be processed simultaneously.
What happens if I exceed my concurrency limit?
What happens if I exceed my concurrency limit?
If you exceed your concurrency limit, you will receive a
429 Too Many Requests error. The system won’t accept additional requests until current tasks complete and free up slots.How can I monitor my available concurrency slots?
How can I monitor my available concurrency slots?
Use the
Concurrency-Remaining header in your API responses to check how many slots are still available for sending new requests.What is the difference between concurrency and rate limiting?
What is the difference between concurrency and rate limiting?
Concurrency refers to the number of tasks handled at once, while rate limiting controls the total number of requests allowed in a set time period. Both can impact the efficiency of your scraping tasks.
How can I handle slow requests and optimize concurrency usage?
How can I handle slow requests and optimize concurrency usage?
To improve efficiency, consider breaking down larger tasks into smaller chunks or optimizing the time each request takes to complete. Faster requests will free up slots more quickly.
If I cancel a request, will it free up the concurrency right away?
If I cancel a request, will it free up the concurrency right away?
No, when you cancel a request, it can take up to 3 minutes for the associated concurrency slot to be freed. If you cancel multiple requests at once, you will need to wait a few minutes before you can fully utilize those freed slots again.